PARP and DDR Pathway Drug Discovery
DNA damage response (DDR) is a normal cellular function that can result in DNA repair, cell cycle arrest, senescence and/or apoptosis in response to cellular DNA damage. Defects in the DDR pathway lead to genomic instability, cancer initiation and uncontrolled cell proliferation. Many kinases such as WEE1, DNA PK and ATM/ATR in the DDR pathway have been pursued as drug targets for cancer therapy. The 17 member Poly (ADP ribose) Polymerase (PARP) family of proteins mediate a number of cellular processes, including gene transcription and DNA repair, and are widely implicated in human disease.
Promega offers a variety of assays and technologies to facilitate PARP/DDR pathway drug discovery. These include target engagement assays to measure compound binding to pathway components, PARP and kinase activity assays and cell health assays.
Interested in more information about PARP/DDR pathway drug discovery solutions?
Interested in more information about our PARP and kinase selectivity compound profiling services?
Numerous signaling networks are associated with DDR mechanisms. These modes involve sensors (e.g., PARPs), mediators (e.g., DNA PK, ATM, ATR), and transducers and effectors of signaling (e.g., kinases). The PARP family of proteins is classified in two groups based on poly vs. mono ADP ribosylation.


Target Engagement
NanoBRET® technology offers a sensitive, specific method to measure the interaction of small-molecule drugs with their target protein in live cells.
With the NanoBRET® Target Engagement Assay, you can:
- Quantitate compound affinity (how tightly it binds to a protein) and target protein occupancy (how much compound binds to a protein) in live cells.
- Assess how long a compound binds to the target protein (its residence time) under physiological conditions.
- Scale the simple, multiwell assay to suit your research throughput needs.
- Generate high‐quality data with low error rates and high reproducibility.
- Get started quickly with available ready-to-use assays.

Principle of the NanoBRET® Target Engagement Assay. Binding of a test compound results in loss of NanoBRET® signal between a target-NanoLuc® fusion protein and a cell-permeable fluorescent NanoBRET® Tracer inside intact cells.
Measure PARP Target Engagement in Live Cells
The NanoBRET® TE PARP Assay can be used to characterize PARP inhibitor selectivity and affinity across multiple PARPs. Intracellular residence time can be evaluated in a simple format, wherein unmodified compound is added prior to tracer addition. After compound washout, the tracer is added and residence time is quantified in live cells.
PARP1 inhibitors are promiscuous against lesser studied PARPs.
FDA-approved and clinical PARP Inhibitors engage a spectrum of mono-PARPs in cells.


Measure Target Engagement of Other DDR Proteins
Our target engagement assays can provide deeper insights into binding affinity and residence time of small molecule interactions with other key DDR proteins in live cells, including PARG, polymerase theta (polQ), and PRMT5.
Want to see more data?

Scientific Poster: Exploring the Landscape of PARP and PARG Inhibitor Selectivity in Live Cells Using NanoBRET® Target Engagement Assays
Want to see more data?

Scientific Poster: A NanoBRET® Target Engagement Assay for Querying Domain Selectivity at Full-Length Polymerase Theta in Live Cells
Want to see more data?

Scientific Poster: A Live Cell PRMT5 NanoBRET® Target Engagement Assay Querying Competitive and Uncompetitive Modes of Inhibition
Measure PARP Activity Using the NAD/NADH-Glo™ Assay
Upon DNA damage, PARP activity is upregulated. Monomeric NAD(+) is consumed and enzymatically polymerized into a Poly ADP ribosylation chain at the site of the damage or a mono ADP ribose added to the target substrate.
The bioluminescent NAD/NADH-Glo™ Assay is a homogeneous assay that detects NAD(+) and NADH and determines their ratios in biological samples such as cell lysates. The simple add-and-read format can be easily adapted for high-throughput screen. A modified protocol is available upon request for measuring activity of PARPs and other enzymes.

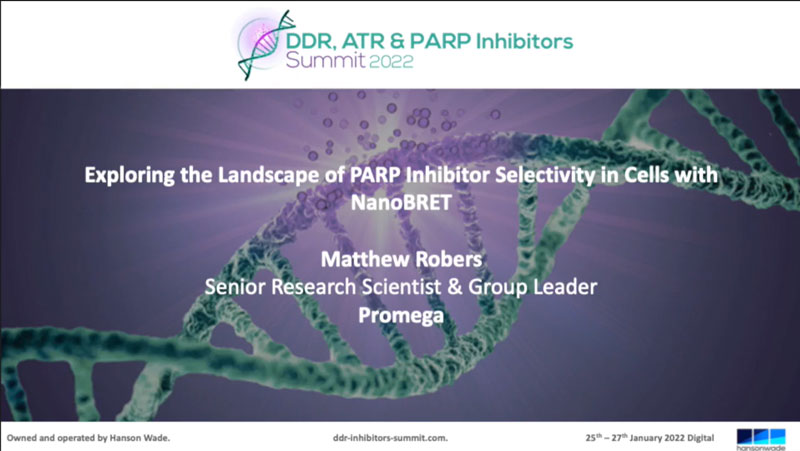
PARP activity assay. PARP1 activity was measured in reactions containing PARP1, 375ng nucleosomes and 20μM NAD in a 384-well plate. After a 1-hour incubation, NAD levels were analyzed by adding an equal volume of modified NAD/NADH Glo™ Detection Reagent. Luminescence was recorded after 20 minutes. Panel A: Titration of PARP1 enzyme (in 5μl volume). Panel B: PARP1 inhibition.
AMP-Glo™ Assay to Measure PARP Activity
The AMP-Glo™ Assay is a homogeneous assay that generates a luminescent signal from any biochemical reaction that produces AMP. It can be used to measure the activity of a broad range of enzymes, such as cyclic AMP specific phosphodiesterases , aminoacyl tRNA synthetases, DNA ligases and ubiquitin ligases or enzymes modulated by AMP.
Read a publication using this assay to monitor Poly ADP ribosylation: Mondal, S., Hsiao, K. and Goueli, S.A. (2017) Utility of Adenosine Monophosphate Detection System for Monitoring the Activities of Diverse Enzyme Reactions. ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 15, 300–341.
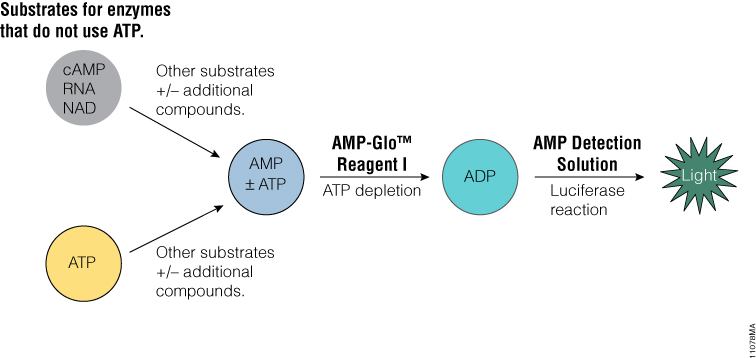
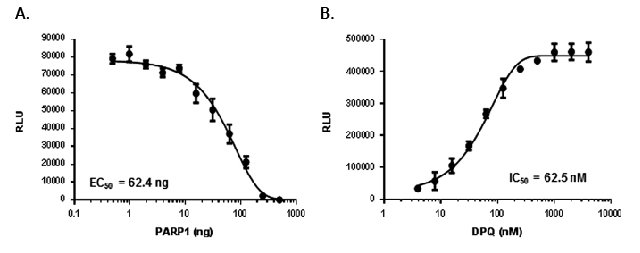
Measurement of ADPribosylation using the modified AMP-Glo™ assay. Panel A: Poly ADP ribosylation of PARP1 on nucleosomes. Reactions containing PARP1 activity was measured using 50μg/ml nucleosomes and 20μM NAD ++, and different amounts of PARP1 were analyzed by the AMP-Glo™ system. Panel B: Detection of PARP1 inhibition by DPQ.
Kinases in DDR
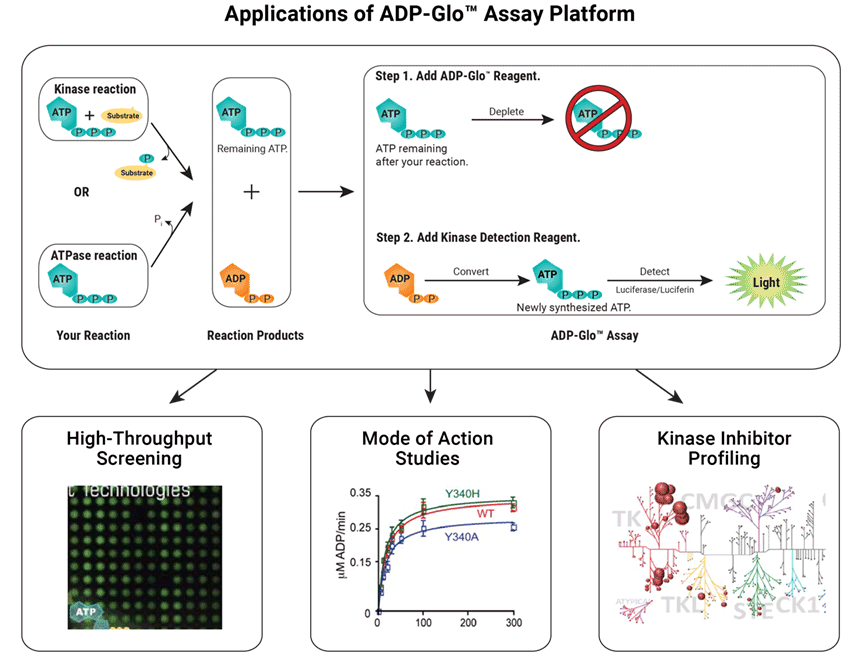
Kinase Selectivity Profiling with the ADP-Glo™ Assay
The ADP-Glo™ Kinase Assay is a Universal in vitro Biochemical Assay for all types of kinase studies. The assay measures ADP formed from a kinase reaction. The ADP is converted into ATP, which is used to generate a stable luminescent signal.
Applications of the ADP-Glo™ Assay include:
- High-throughput screening
- Mode of action studies
- Kinase inhibitor profiling
Kinase Enzyme Systems, which are optimized for use with the ADP-Glo™ Assay, allow you to easily screen and profile kinase inhibitors. The following kinases related to the DNA Damage Response are available:
Live-Cell Target Engagement
The NanoBRET® Target Engagement (TE) Kinase Assays allow you to quantitate compound binding to full length kinases inside live cells. Assays are available for >340 kinases with individual application notes for each kinase, including many kinases involved in DDR (e.g., CHK1, CHK2, CDK2/ Cyclin A1, CDK2/Cyclin E1, CDK6/Cyclin D, PKMYT1, PLK family, CK2 α isoforms, MAPKAPK2 (MK2), MARK3, Wee1). Individual application notes are available for each kinase. View the Kinase Target Engagement Assay Selection Guide for a complete list of available kinases.





DDR kinase inhibitor selectivity in live cells, compared to cell-free analysis.
Detection of Total or Phosphorylated Cellular Targets
Study Signaling Nodes in DNA Damage Response Using Lumit® Immunoassay Cellular Systems
The Lumit® Immunoassay Cellular System is a no-wash bioluminescent immunoassay that measures target analytes directly in cell lysates. The assay can be customized to detect nodes of signaling involved in DNA damage response using a simple workflow that doesn’t require media removal or lysate transfer. Simply add labeled antibodies to the sample, add the detection reagent and read the luminescent signal—all in a single plate.
Download this poster to see the data: Detection of DNA Damage Response Pathway Marker Activation Using Lumit Immunoassays





DNA Damage Response Pathway Markers. Lumit® Immunoassays demonstrate activation and inhibition of cellular CHK1 and H2AX phosphorylation. Panel A and C. Detection of Etoposide induced phosphorylation of H2AX in A549 cells using the Lumit® Immunoassay Cellular System. Phosphorylation is inhibited with ATM kinase inhibitors, but not ATR inhibitors. Download H2AX Application Note for details. Panel B and D. Detection of Hydroxyurea-induced phosphorylation of CHK1 in SW620 cells using the Lumit® Immunoassay Cellular System. ATR inhibition, but not ATM inhibition, reduces CHK1 phosphorylation. Download CHK1 Application Note for details.
Cell Viability Assays
Measure Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity
We offer an extensive portfolio of assays to measure cell viability. These automation friendly, real-time and endpoint assays allow simple, add mix read formats and are ideal for secondary screening and lead optimization. Measure the effects of drug candidates on cell health and cytotoxicity in live cells including cells in 3D culture.
The CellTiter Glo® 2.0 Cell Viability Assay is a highly sensitive assay with broad linearity. It is scalable to 384-well and 1,536-well plates for high-throughput primary screening applications.
See how these cell health assays have been applied to DDR in these publications.
Selected References:
- Zimmermann, M. et al. (2022) Guiding ATR and PARP inhibitor combinations with chemogenomic screens. Cell Reports. 40, 111081.
- Kim, C. et al. (2020) PARP1 inhibitors trigger innate immunity via PARP1 trapping induced DNA damage response. eLife August 26, e60637.
- Blessing, C. et al. (2020) The oncogenic helicase ALC1 regulates PARP inhibitor potency by trapping PARP2 at DNA breaks. Mol. Cell. 80, 862–875.
Profiling Services
Our custom assay services can help to accelerate your small and large molecule drug discovery and development workflow. These comprehensive services are built around our technologies for sensitive, high throughput and biologically relevant results. For more information, contact the Tailored R&D Solutions team.
PARP Compound Selectivity Profiling Service
- Selectivity profiling in live cells using NanoBRET® TE assays against 12 PARP family members
- Ratiometric BRET data provide reproducibility with low error rates
Kinase Cellular Selectivity Compound Profiling Service
- Selectivity profiling in live cells using NanoBRET® TE assays against 240 kinases
- Ratiometric BRET data provide reproducibility with low error rates