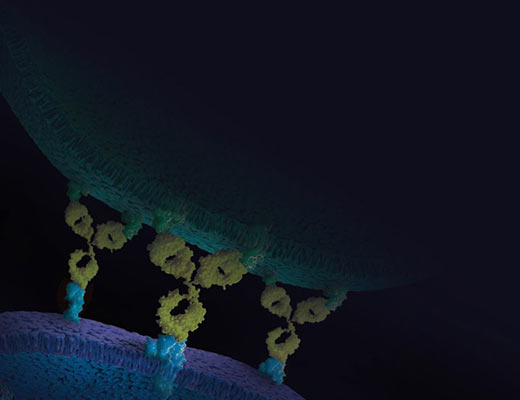
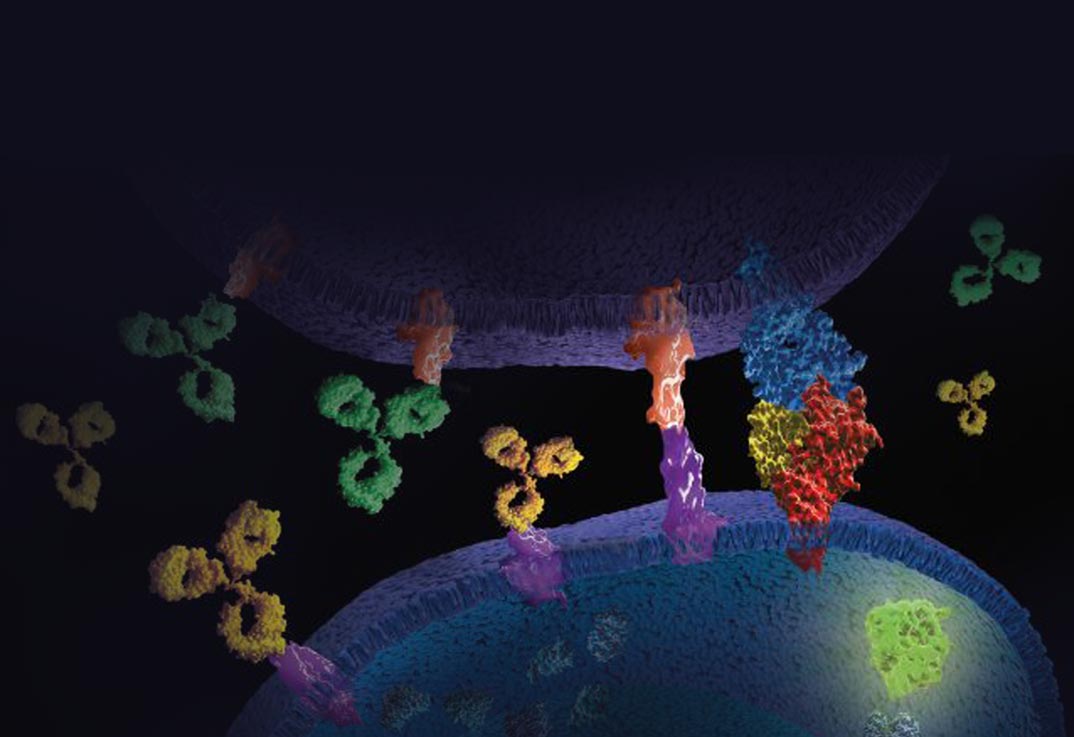
Immune Checkpoint Bioassays
Our industry leading bioassays can accelerate your immunotherapy drug development. Whether you’re targeting immune checkpoint co-inhibitory, co-stimulatory, or a combination of receptors, we have the tools to meet your needs. Our robust collection of assays can be used in a variety of settings, from antibody screening and characterization, to potency and stability determination and QC lot release.
Filter By
Shop all Immune Checkpoint Bioassays
Showing 24 of 24 Products
Featured Publications
LAG-3/MHCII Blockade Bioassay
Ghosh, S. et al. (2019) TSR-033, a novel therapeutic Ab targeting LAG-3, enhances T-cell function and the activity of PD-1 blockade in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 18, 632–641. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0836
PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Bioassay
Rattanapisit, K. et al. (2019) Structural and in vitro functional analyses of novel plant-produced anti-human PD1 antibody. Sci. Rep. 9, 15205. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51656-1
CTLA-4 Blockade Bioassay, PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Bioassay, OX40 Bioassay
Simons, J.F. et al. (2020) Affinity maturation of antibodies by combinatorial codon mutagenesis versus error-prone PCR. mAbs 12(1), 1803646. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2020.1803646
An Introduction to Immune Checkpoint Receptors
The immune system is comprised of a complex network of co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory pathways that help to maintain homeostasis and prevent autoimmunity. Under typical conditions, these immune checkpoints allow appropriate immune response to infections and malignancies while protecting healthy tissues from harm.
Inhibitory immune checkpoint receptors (including PD-1, CTLA-4, TIGIT, LAG-3, and TIM-3) expressed on activated T cells and B cells play a critical role in regulating immune responses to tumor antigens and autoantigens. Engagement of a receptor by its ligand on an adjacent cell inhibits T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling and TCR-mediated proliferation, transcriptional activation and cytokine production. Therapeutic antibodies and Fc fusion proteins designed to block the receptor-ligand interaction show promising results in clinical trials for the treatment of a variety of cancers.
Co-stimulatory immune checkpoint receptors (including GITR, OX40, CD40, 4-1BB, and ICOS) are expressed on T cells. Therapeutic antibodies designed to activate these immune checkpoint receptors and enhance immune signaling are also emerging as a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
Cell-based functional reporter bioassays are critical to the development and characterization of antibody based biologic drugs targeting immune checkpoint receptors.