Automated extraction of gDNA from blood using the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex Instrument
Sarah Teter and Doug Wieczorek
Promega Corporation
Publication Date: September 2017, tpub_188
Abstract
This article describes an automated method for the extraction of high quality gDNA from freshly collected blood or previously frozen blood using the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument.
Introduction
This application note describes an automated method for the extraction of genomic DNA (gDNA) from up to 96 samples of a 250µl volume of blood using the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument. The purified gDNA can be used directly in many downstream applications. The use of paramagnetic particles makes the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System suitable for full automation on the KingFisher™ Flex. In addition, the system does not require phenol or chloroform, making it safe and convenient.
The Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System uses Proteinase K and a specially formulated Cell Lysis Buffer to liberate sample DNA. Released DNA is bound to the resin particles in the presence of the Binding Buffer. The DNA bound to resin is captured by a magnet and contaminants are removed by washing with the Wash Buffer and ethanol. The DNA is then eluted from the particles with 25mM Tris-HCl. The process involves the following simple steps:
- Cell lysis with Proteinase K and Lysis Buffer
- gDNA capture to paramagnetic resin in Binding Buffer
- Washes with Wash Buffer and ethanol
- Elution with Tris-HCl
The automated method can be used for extraction of high quality gDNA from freshly collected blood or previously frozen blood. This protocol is developed for research use only, and the user will need to assess the applicability of this protocol for his or her needs.
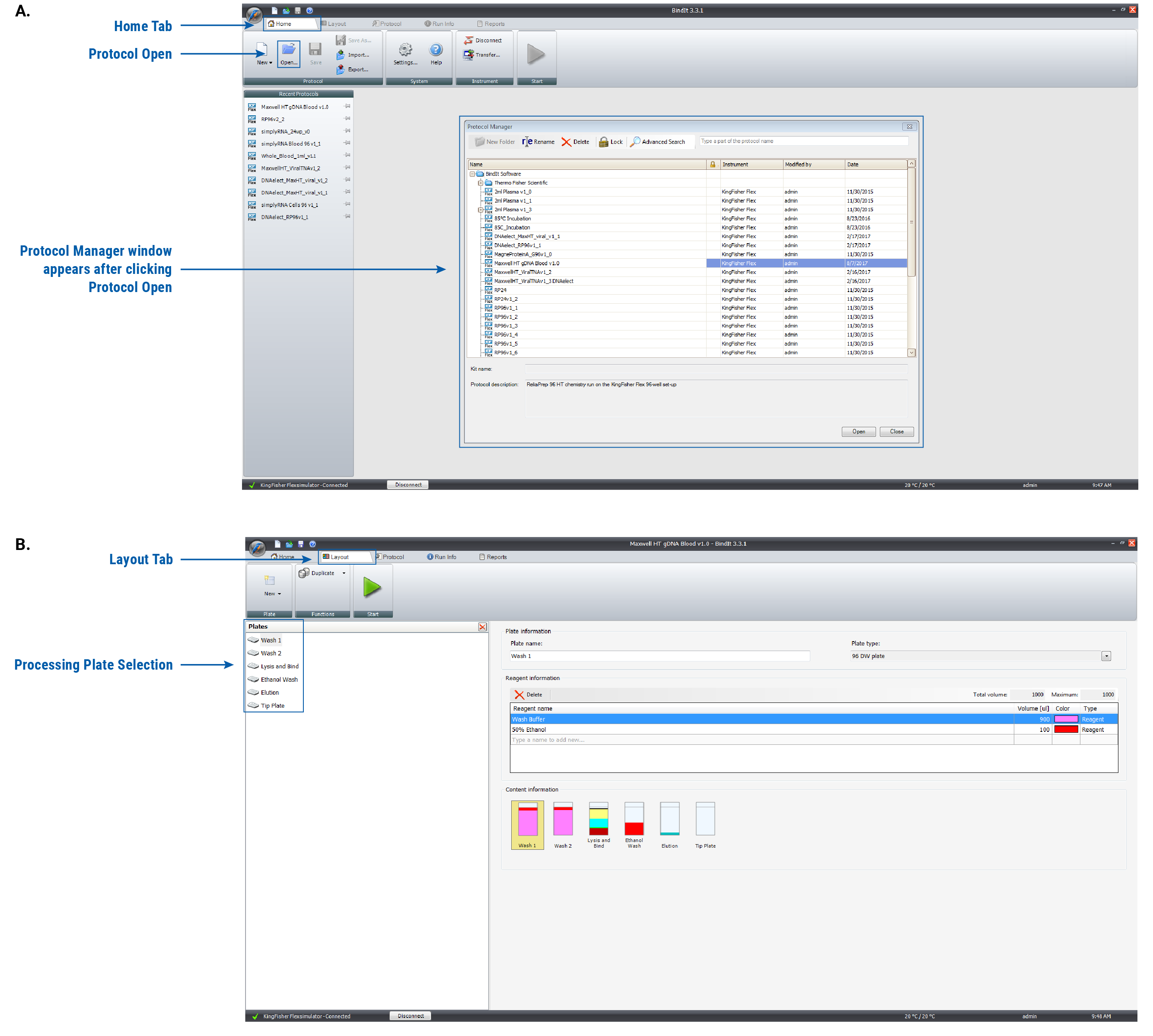
Figure 1. Navigation in the BindIt™ Software. Panel A. Loading the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method. From the Home Tab, click the Protocol Open icon to open the Protocol Manager window. Select the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method and select Open in the Protocol Manager window to launch the method. Panel B. Determining the processing plate layout for the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method. Under the Layout tab, you can view each processing plate and select different plate options from the left window to see which reagents are added to each processing plate.
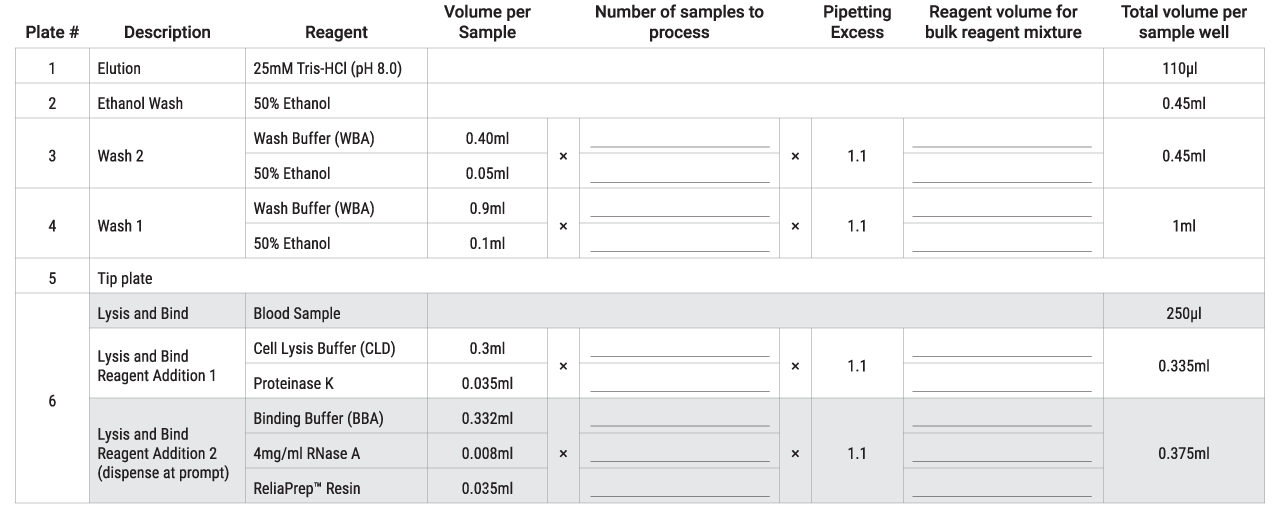
Table 1. Volumes of reagent to prepare for each processing plate. Thoroughly vortex all solutions of bulk reagent mixture before adding to the plate.
Materials and Methods
- Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System (Cat.# A2670, A2671)
- 47.5–50% ethanol (Note: Prepare by diluting 95–100% USP/ACS- or molecular biology-grade ethanol with an equal volume of molecular biology-grade water. Using denatured ethanol that contains methanol or isopropanol may decrease DNA purity or yield.)
- Pipettes and tips for filling plates with extraction reagent (Note: Use of repeater pipettes can increase efficiency when filling plates.)
System requirements: KingFisher™ Flex Purification System equipped with the KingFisher™ Flex Head for Microtiter Deep Well 96 plate and Heating Block for Microtiter 96 Deep Well Plate. The BindIt™ Software Package provided with the KingFisher™ Flex will also be required to transfer the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood v1.0 method to the instrument. To download the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood v1.0 method, contact Technical Services: techserv@promega.com.
The following consumables are required for each automated extraction:
- KingFisher™ 96 Tip Comb for Deep Well Magnets (ThermoFisher Scientific Cat.# 97002534)
- KingFisher™ Deep Well 96 Plate, V-bottom, polypropylene (ThermoFisher Scientific Cat.# 95040450) – 6 plates per extraction
Caution: We recommend the use of gloves, lab coats and eye protection when working with these and any chemical reagents.
Sample handling recommendations: For fresh blood, we recommend storing at 4°C for no longer than 48 hours prior to processing. For frozen storage of blood, we recommend storing at –80°C for no longer than one month prior to processing for extraction of gDNA.
Import the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method into the BindIt™ Software and transfer the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method onto the KingFisher™ Flex as described in the Thermo Scientific BindIt™ Software Guide. The Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method will guide you through the preparation of reagent plates for the run. The steps to prepare for a gDNA extraction from blood are outlined below.
- Ensure that the KingFisher™ Flex is set up with the KingFisher™ Flex Head for Microtiter Deep Well 96 Plate and Heating Block for Microtiter 96 Deep Well Plate. Refer to the directions in the KingFisher™ Flex User Manual to change either the Flex Head or Heating Block, if necessary.
- Load the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method from the Protocol Manager in the BindIt™ Software. The Protocol Manager is accessed by clicking the Open icon in the Protocol menu of the Home tab (as outlined in Figure 1, Panel A). In the Protocol Manager window that appears, select the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method and select “Open” to launch the method.
- Label six 96 Deep Well Plates accordingly.
Plate 1 – Elution
Plate 2 – Ethanol Wash
Plate 3 – Wash 2
Plate 4 – Wash 1
Plate 5 – Tip Plate
Plate 6 – Lysis and Bind - Prepare Plate 5 – Tip Plate. Slide a KingFisher 96 Deep Well Tip Comb into a KingFisher Deep Well 96 Plate.
- Prepare the Plate 4 – Wash 1, Plate 3 – Wash 2, Plate 2 – Ethanol Wash and Plate 1 – Elution processing plates. Table 1 can be used to calculate the volumes of reagents to be added to each well of the processing plates. The reagent volumes to be added to the processing plates can also be found in the BindIt™ Software, as described in Figure 1, Panel B.
Note: To expedite the setup of the sample plates, we recommend that you prepare a bulk reagent mixture for each well, depending on the number of samples that are being run. A repeater pipette may be used to add the bulk mixed reagent to each well of the plate. - Add 250µl of the blood samples to Plate 6 – Lysis and Bind Plate.
- Add the indicated volume of Lysis Buffer (CLD) and Proteinase K to the sample wells in Plate 1 – Lysis and Bind Plate. The Lysis Buffer (CLD) and Proteinase K can be added separately. Alternatively, you can prepare a bulk reagent mixture of Lysis Buffer (CLD) and Proteinase K to be added to the plate. The Prepared Binding Buffer and resin will be added to the Lysis and Binding Plate later.
Notes:
If using, prepare the bulk reagent mixture of Lysis Buffer (CLD) and Proteinase K just prior (<10 minutes) to adding the mixture to your blood samples.
After the Lysis Buffer (CLD) and Proteinase K are dispensed into the wells containing blood samples, the processing plates should be loaded onto the KingFisher™ Flex and therun should be started immediately. - Start the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method. If the KingFisher™ Flex is being run through a connected PC with the BindIt™ software, you can simply load the Maxwell HT gDNA Blood v1.0 method and press the Start button to begin loading the processing plates. If the instrument is being run from the internal software, find the method in the list of User Defined Protocols and press the Start button on the instrument to begin loading the plates. Place the indicated plate in the Loading Station of the instrument, then press the Start button to load the next plates until all plates are loaded. Once all plates are loaded, you can close the sliding door of the Loading Station.
- Add the Binding Buffer (BBA), RNase A and resin to each sample in Plate 1 – Lysis and Bind when prompted by the software. Prepare a bulk reagent mixture of Binding Buffer (BBA), RNase A and resin, according to your calculations in Table 1. After about 25 minutes of runtime, the software will pause and prompt for the addition of the Binding Buffer (BBA), RNase A and resin to the plate. Open the sliding door and remove the plate from the Loading Position of the KingFisher™ Flex. Add 375µl of the Binding Buffer (BBA), RNase A and resin mixture to the wells of the Lysis and Binding Plate containing sample. Return the plate to the instrument and press “Run” to resume processing.
Note: The resin must be mixed to a homogeneous suspension before addition to the bulk reagent mixture with Binding Buffer A (BBA) and resin. Also, before dispensing the Binding Buffer (BBA), RNase A and resin bulk reagent mixture to the Lysis and Bind Plate, vortex the solution for 5 seconds to ensure resin suspension. Continue to shake/vortex the mixture from time to time while adding it to the samples in Plate 1 – Lysis and Bind. - Once the run has ended, remove the elution plate from the deck and clean up the other processing plates. Waste should be discarded per your institution’s biohazardous waste instructions. The eluate can be used immediately or stored as appropriate for later analysis.
Results
High yields and high purity DNA recovered using the Maxwell® HT gDNA extraction method on the KingFisher™ Flex.
Due to the biological variation of blood from different individuals, it was important to test whether the method could be used to recover high purity DNA across samples obtained from different individuals. We extracted gDNA from 250µl fresh whole blood from 10 individuals or previously-frozen blood from 10 individuals with a white blood cell (WBC) count within the normal range of 4–11 × 106 WBC/ml. The yield was calculated from the UV absorbance at 260nm and normalized to the WBC count for each of the samples (Figure 2). All of the samples processed gave a yield of 3.0pg/WBC or greater, demonstrating efficient recovery of gDNA from blood using the automated method on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument. The purity of the isolated gDNA was assessed by UV absorbance ratios (Figure 2). Typically, pure gDNA is defined by A260/A280 ratios greater than 1.7 and A260/A230 ratios of 1.8–2.2. All of the samples that were purified had absorbance ratios within the ideal range, indicating highly pure DNA was extracted. Additionally, gel electrophoresis of the extracted gDNA resulted in a strong single band (>23 Kbp) for all samples, indicating that the gDNA that was extracted was largely intact (data not shown).

Figure 2. gDNA recovery from blood using the Maxwell® HT gDNA Blood System on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument. Panel A. Fresh blood was used as the input sample for extraction using the Maxwell® HT gDNA Blood System on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument. Panel B. Frozen blood from 10 individuals was used as the input sample for extraction using the Maxwell® HT gDNA Blood System on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument. The gDNA recovery (pg/WBC), represented by the blue bars, was calculated from the sample concentration and normalized to WBC count. UV absorbance ratios, A260/A280 (blue points) and A260/A230 (yellow points) are plotted on the secondary y-axis. Error bars represent the standard deviation of four extractions for each sample.
Robust DNA recovery between analysts and in separate extractions.
We assessed whether the performance of the gDNA extraction using the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex would be consistent between extractions performed by a single analyst over three days as well as separate extractions performed by three individual analysts. Single-source frozen human blood was used across this set of experiments to minimize differences in recovery or purity resulting from the biological variability. Following gDNA extraction from 250µl of blood, UV absorbance at 260nm was measured for sample concentration. The coefficient of variability (%CV) for the yield/WBC was ≤10% for gDNA extractions performed by a single analyst over three days and gDNA extractions performed by three individual analysts, as seen in Tables 2 and 3. This indicates that the automated purification method for Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex gives reproducible extraction performance.
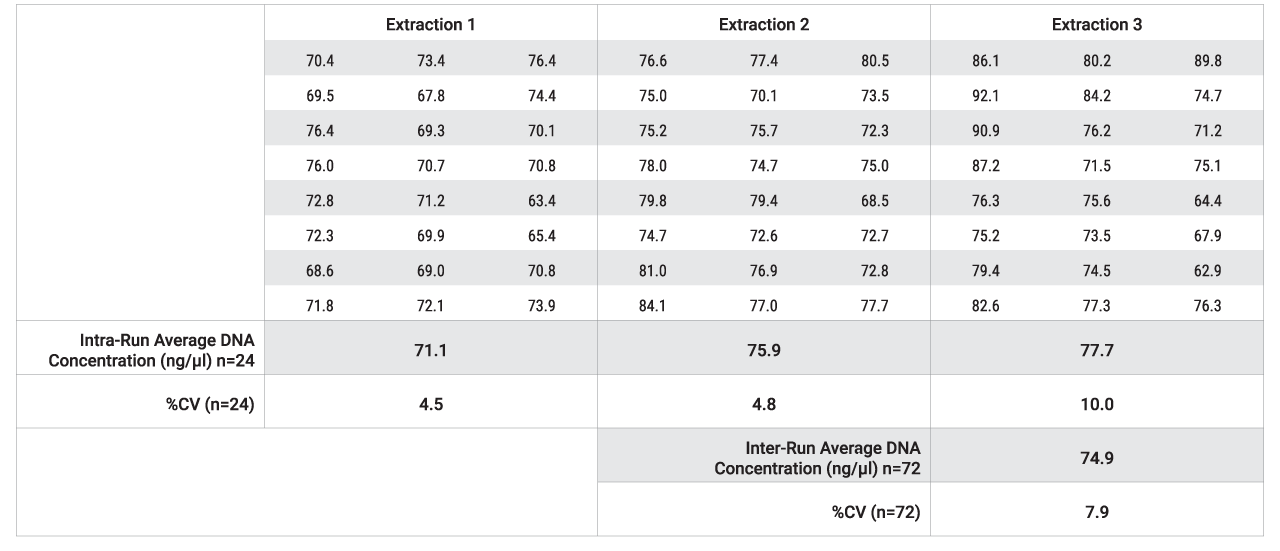
Table 2. Consistency of extractions performed over three days by a single analyst. 250µl of blood from a single donor was extracted using the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex over three days. Following extraction, the concentration (ng/µl) of the samples was determined by UV absorbance at 260nm using the NanoDrop™ One Microvolume UV-Vis Spectrophotometer.
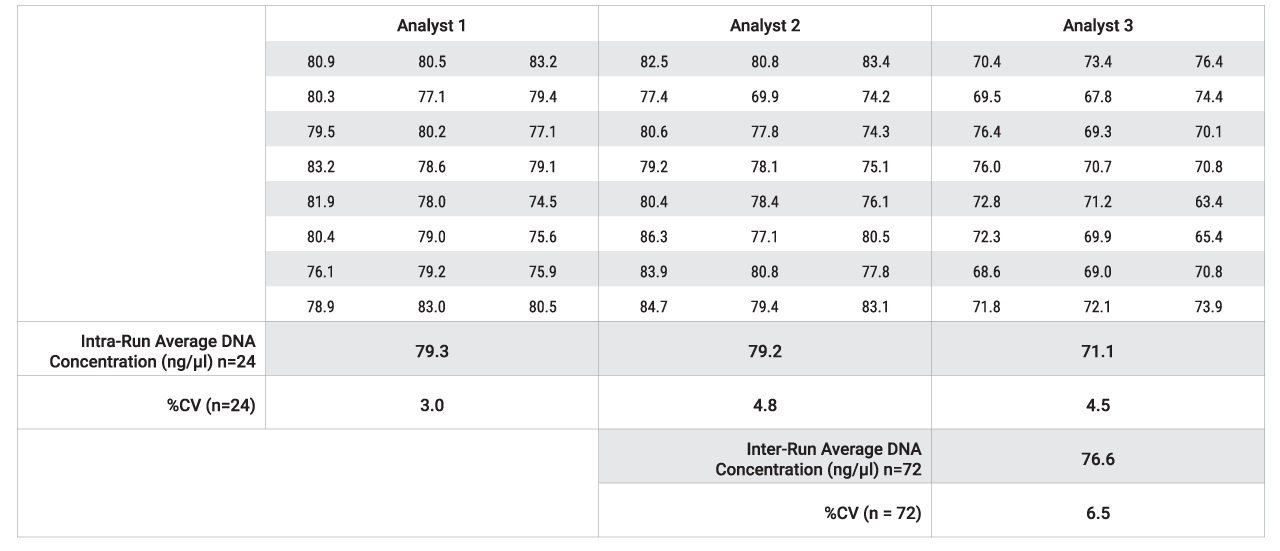
Table 3. Consistency of extractions performed by three analysts. 250µl of blood from a single donor was extracted by three analysts using the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex. Following extraction, the concentration (ng/µl) of the samples was determined by UV absorbance at 260nm using the NanoDrop™ One Microvolume UV-Vis Spectrophotometer.
No detectable cross-contamination of samples.
Potential well-to-well cross-contamination due to sample processing on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument was monitored using the PowerQuant® System (Cat.# PQ5002). The PowerQuant® System is a sensitive real-time PCR assay that can be used to determine the amount of amplifiable autosomal and Y-chromosomal DNA in a single assay. To test for potential sample cross-contamination during extraction, we processed 250µl blood from male and female sources loaded in a checkerboard pattern across the deep-well 96 plate (see Figure 3, Panel A). The samples were extracted using the automated method for Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex instrument. Detection of the male Y DNA in the gDNA extracted from female blood would indicate cross-contamination from the adjacent wells containing male blood. As seen in Figure 3, Panel B, all of the extracted female gDNA samples contained either undetectable amounts of the Y allele or the concentration of the Y allele was significantly lower than the lowest point on the PowerQuant® System standard curve (3.2pg). This demonstrates that the automated extraction procedure does not introduce sample-to-sample cross-contamination.

Table 4. Assessing cross-contamination during the automated purification method. Panel A. Representation of the layout of the male and female blood in the sample plate. Panel B. The detected concentration (ng/µl) of the Y allele in the extracted gDNA samples. ND indicates that there was no detectable amplification in triplicate amplifications of each sample.
Conclusion
The data presented demonstrate that extraction of gDNA from 250µl of blood using the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System on the KingFisher™ Flex offers the following benefits:
- Up to 96 samples of a 250µl volume of blood can be processed for gDNA extraction in a single 1.5 hour run.
- gDNA extraction is efficient and reproducible using the automated extraction method.
- The extracted gDNA is exceedingly pure and of high molecular weight.