Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) Instruments
The Spectrum CE instruments are designed to address the everyday challenges faced in various laboratory environments, offering scalable solutions for DNA fragment analysis, whether it's for high-throughput needs or more compact setups.
With support for 8- dye technology and compatibility with existing 4-, 5-, and 6-dye kits, these systems cater to diverse applications, including cell line and mixed sample analysis. Additionally, Spectrum Compact is designed for Sanger sequencing, NGS workflows, and CRISPR-Cas9 confirmation, providing flexibility for a wide range of research and analysis needs.
Spectrum CE Systems Comparison
Spectrum CE System |
Spectrum Compact CE System |
|
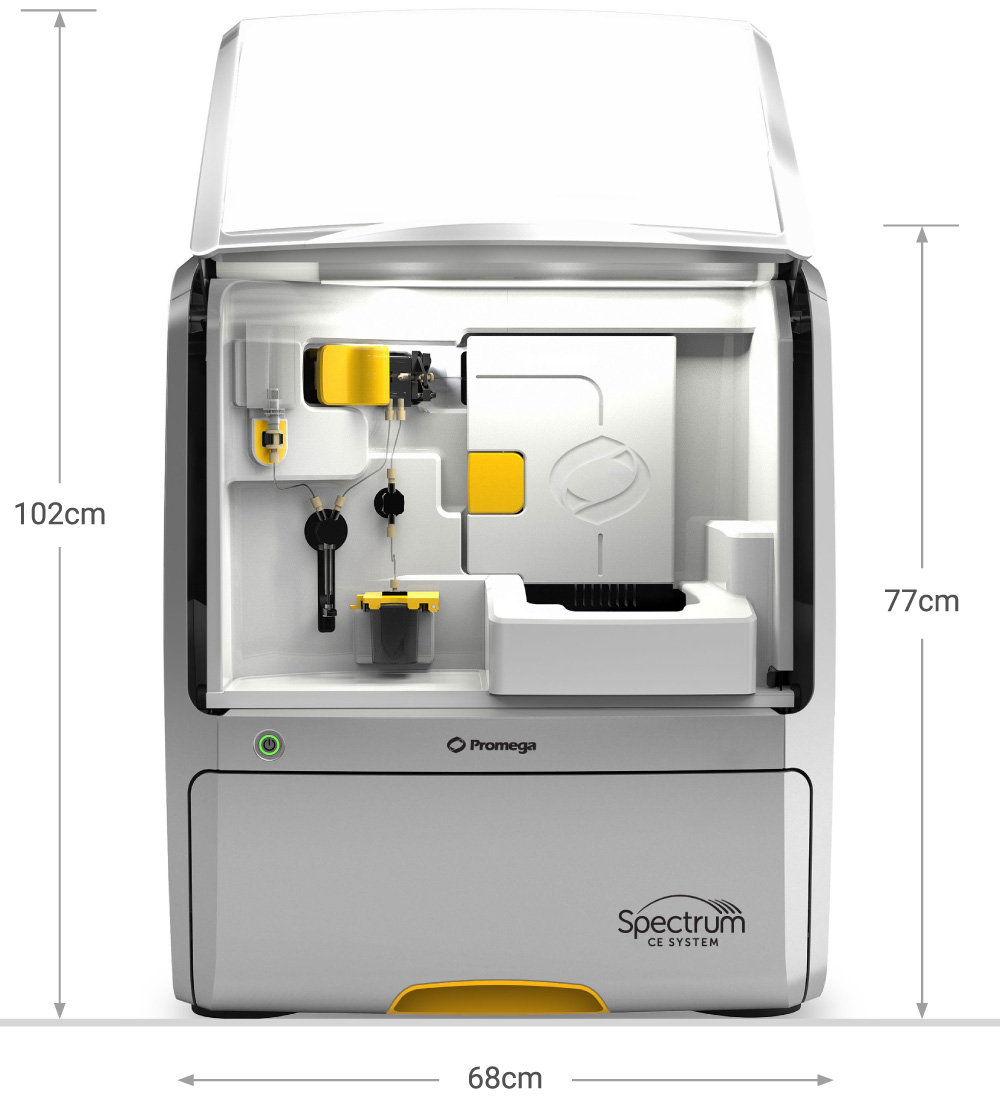 Cat.# CE1008 |
 Cat.# CE1304 |
|
| General Features | ||
|---|---|---|
| Overview |
|
|
| Colors Detected |  |
 |
| Positions | ||
| Position Accessibility | ||
| Sample Vessel Type |  |
|
| Capillary Array Length | ||
| Consumable Bar Code Detection | ||
| Applications | ||
| Consumables | ||
| Buffer | ||
| Polymer | ||
| Wash | ||
| Array | ||
| Tracking | ||
| Polymer Type | ||
| Software | ||
| Export File Type (STR) | ||
| Secondary Analysis Packages | ||
| Technical Specifications | ||
| Polymer Delivery | ||
| Oven Temperature Range | ||
| Electrophoresis Voltage | ||
What is Capillary Electrophoresis?
Capillary electrophoresis is a method for separating and identifying fragments of fluorescently-labeled DNA by passing them through very thin polymer-filled capillaries. The use of capillaries instead of a conventional slab gel makes it possible to apply a much stronger electric field, resulting in faster separation and higher throughput. The process features single-base resolution and requires small sample quantities.
Fluorescently labeled DNA samples are prepared for electrophoresis and loaded into the CE instrument. The capillary array is filled with polymer and placed into the sample wells. When the capillary array enters the wells, an electric current is formed, and the DNA fragments are moved electrokinetically into the capillaries. Next, the ends of the capillary array are inserted into the cathode and anode buffer. The instrument applies a specific voltage and temperature to control sample migration through the capillary array. The fragments are separated by size, with the smallest fragments moving fastest.
The final step is sample detection. As the fluorescently labeled fragments move past the detection window, a laser excites the fluorescent dyes. The emitted light is spectrally separated and recorded by a CCD camera. The CCD camera records the fluorescent signature of each fragment, as well as the elapsed time for the fragment to migrate through the polymer. The raw data is sent to the collection software in the form of a peak and is now ready for analysis.
Applications include STR analysis and Sanger Sequencing, as well as many other everyday functions of both forensic, academic and clinical research laboratories.

What is Sanger Sequencing?
Sanger sequencing, also known as the chain termination method, is a DNA sequencing technique that relies on selective incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides during DNA replication, enabling precise determination of nucleotide sequences. Though newer high-throughput methods have emerged, Sanger sequencing remains a gold standard for small-scale sequencing applications due to its accuracy and reliability. It is widely used for applications such as gene validation, mutation detection, microbial identification, and confirming next-generation sequencing (NGS) results.
What is Fragment Analysis?
Fragment analysis is a molecular biology technique used to separate and analyze DNA fragments based on their size. Utilizing fluorescent labeling and capillary electrophoresis, this method allows for the precise sizing of DNA fragments differing by as little as a single nucleotide. Fragment analysis is essential in applications such as forensic casework, database sample analysis, microsatellite characterization, genotyping, mutation detection, and DNA fingerprinting.
