Module 4 - Evaluating Antiproliferative vs. Cytotoxic Effects

Differentiating Antiproliferative from Cytotoxic Effects
Multiplexing cell health assays can reveal critical information regarding mechanisms of action. For example, whether cells are dying from apoptosis or necrosis, and how you can distinguish nonproliferation from cell death.
Test Your Knowledge With These Four Experiments
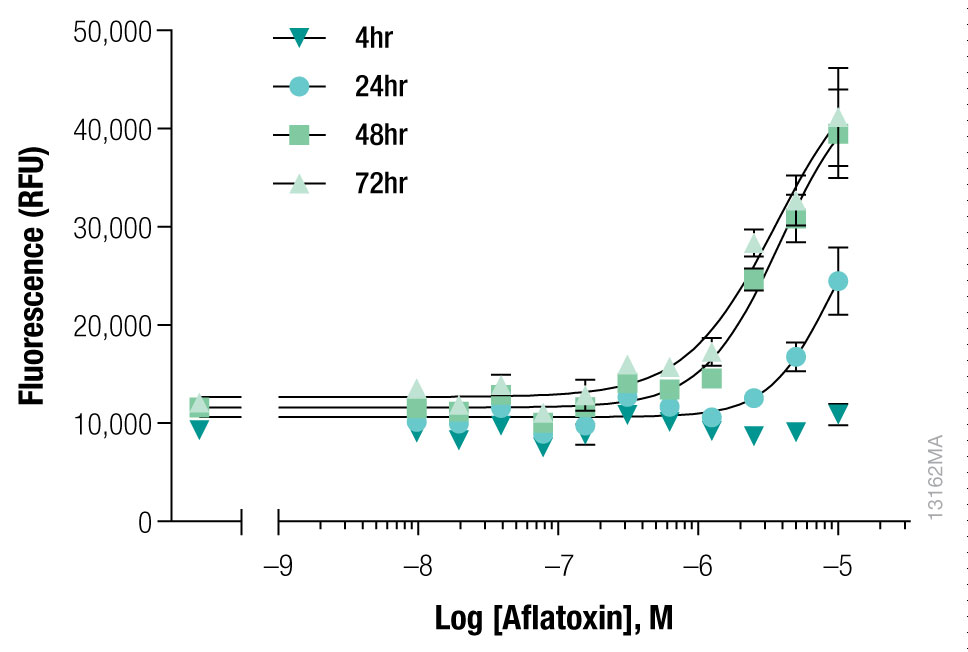
Aflatoxin B1 is a protoxin that requires biotransformation to become toxic. iCell Hepatocytes were treated with Aflatoxin B1. The cell response was evaluated over the course of 72 hours using the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay.
 Interpret The Data
Interpret The Data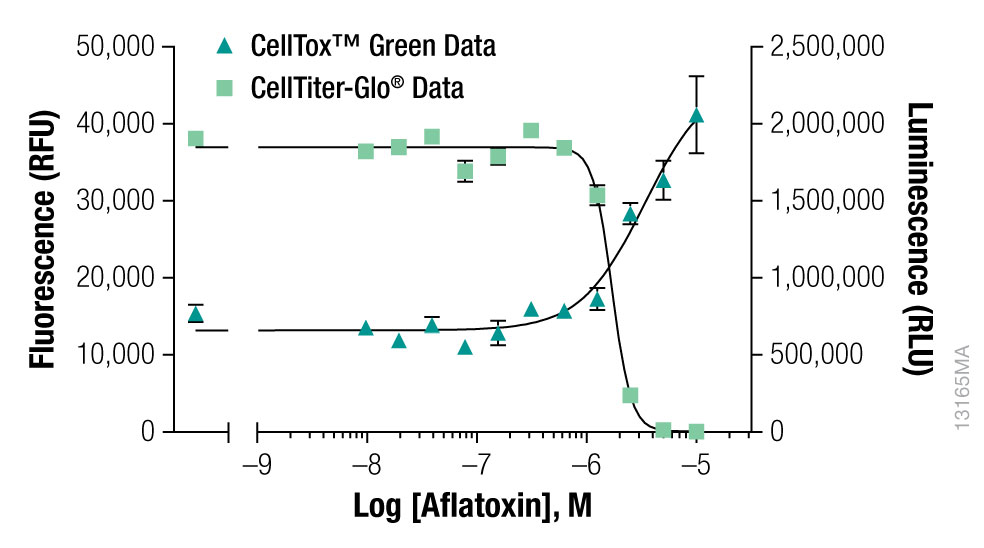
At the 72-hour time point CellTiter-Glo® Cell Viability Assay Reagent was added to determine the number of viable cells by quantifying ATP. Cytotoxicity was determined by using the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay to measure membrane integrity.
 Interpret The Data
Interpret The DataWhat can be determined about this compound's mechanism of action?
(Select more than one answer)
The compound is cytotoxicThe compound is antiproliferative, but not cytotoxic
The compound affects cell viability
The compound does not affect cell health
Check Your Answer
 Drew Explains The Answer
Drew Explains The AnswerEvaluating Mechanism of Action for Aflatoxin B1

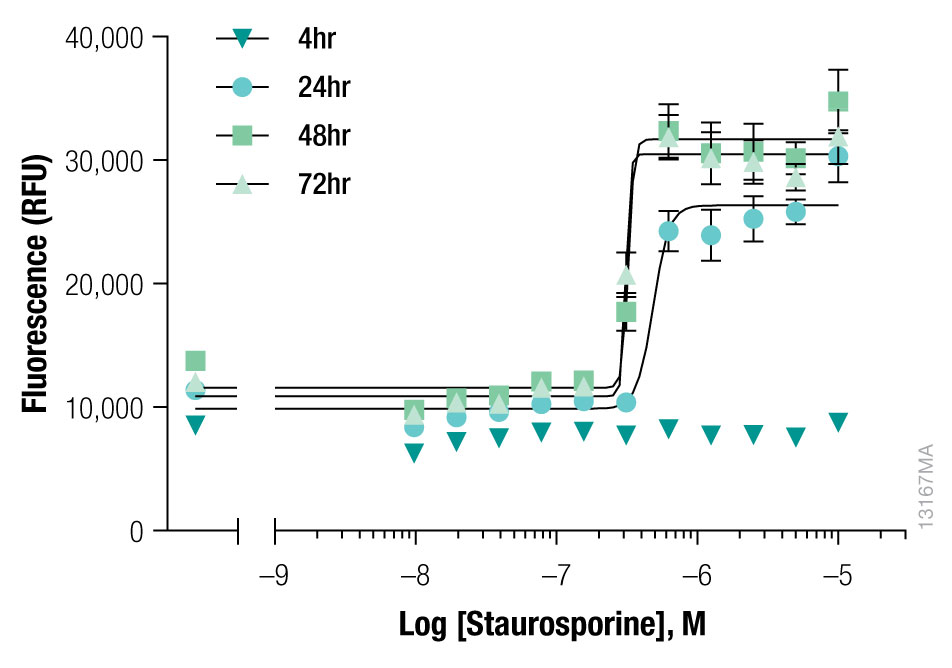
iCell Hepatocytes were treated with Staurosporine (a protein kinase inhibitor). The cell response was evaluated over the course of 72 hours using the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay.
 Interpret The Data
Interpret The DataBased on the data shown, what is the earliest time point where a cytotoxic response is detected?
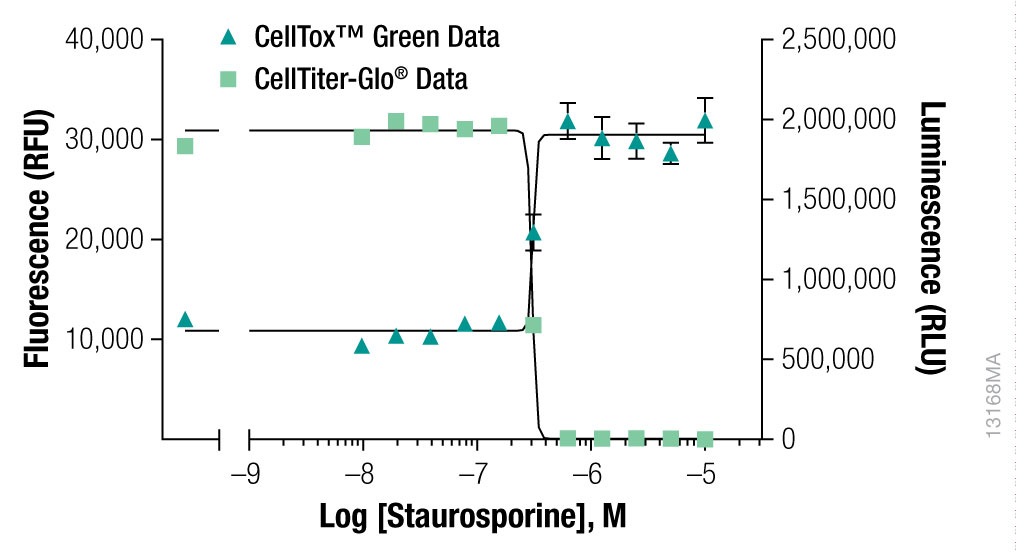
At the 72-hour time point CellTiter-Glo® Cell Viability Assay Reagent was added to determine the number of viable cells by quantifying ATP. Cytotoxicity was determined by using the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay to measure membrane integrity.
 Interpret The Data
Interpret The DataWhat can be determined about this compound's mechanism of action?
(Select more than one answer)
The compound is cytotoxicThe compound is antiproliferative, but not cytotoxic
The compound affects cell viability
The compound does not affect cell health
Check Your Answer
 Drew Explains The Answer
Drew Explains The AnswerEvaluating Mechanism of Action for Staurosporine

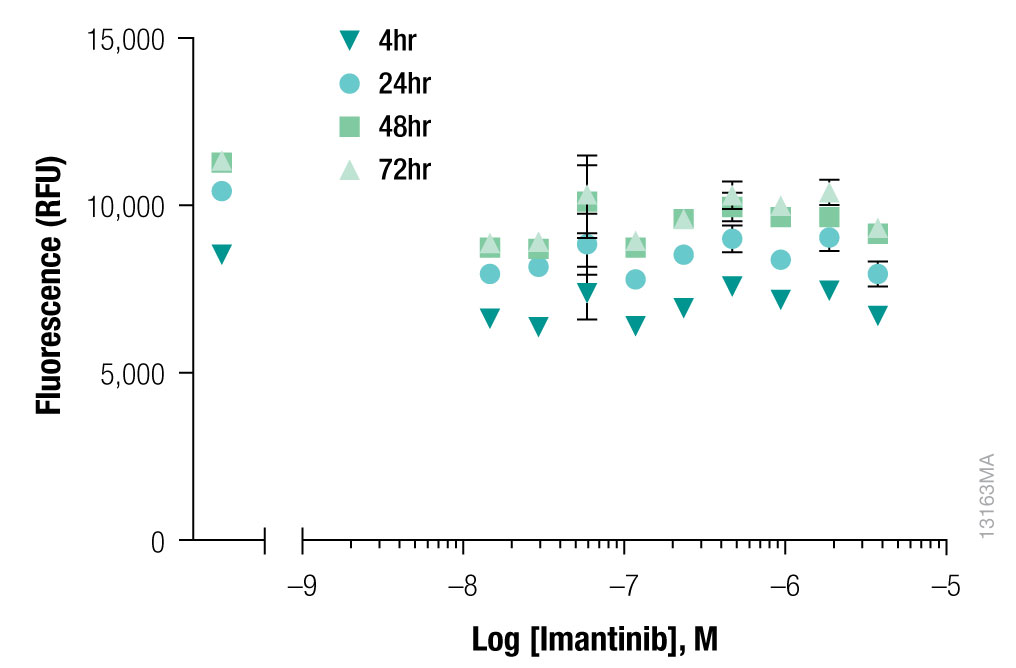
Many drugs exhibit different mechanisms of action when their effect is evaluated on different cell types. iCell Hepatocytes were treated with Imantinib (a kinase inhibitor). The cell response was evaluated over the course of 72 hours using the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay.
 Interpret The Data
Interpret The DataBased on the data shown, what is the earliest time point where a cytotoxic response is detected?
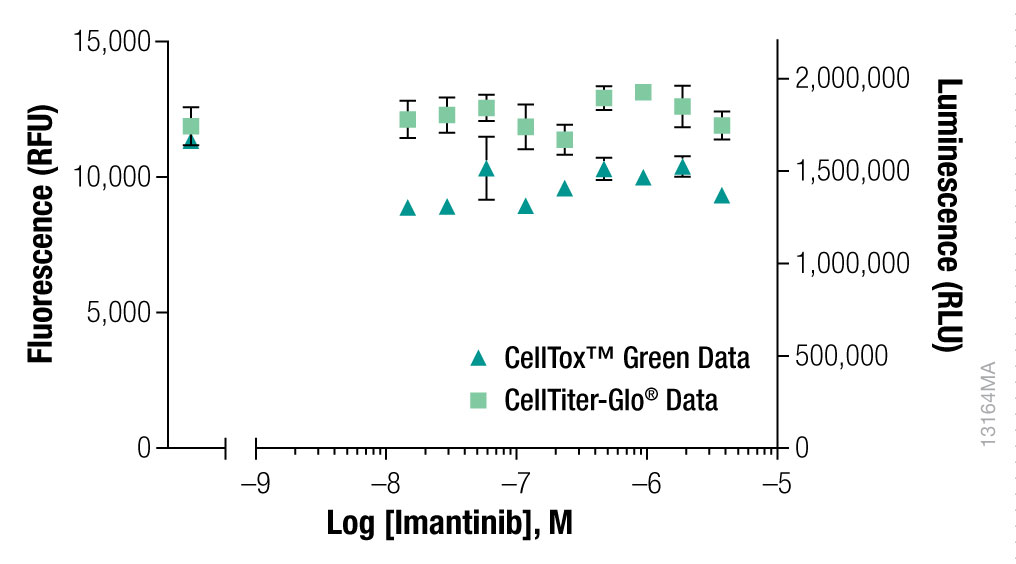
At the 72-hour time-point CellTiter-Glo® Cell Viability Assay Reagent was added to determine the number of viable cells by quantifying ATP. Cytotoxicity was determined by using the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay to measure membrane integrity.
 Interpret The Data
Interpret The DataWhat can be determined about this compound's mechanism of action?
(Select more than one answer)
The compound is cytotoxicThe compound is antiproliferative, but not cytotoxic
The compound affects cell viability
The compound does not affect cell health
Check Your Answer
 Drew Explains The Answer
Drew Explains The AnswerEvaluating Potential Off-Target Toxicity of Imantinib

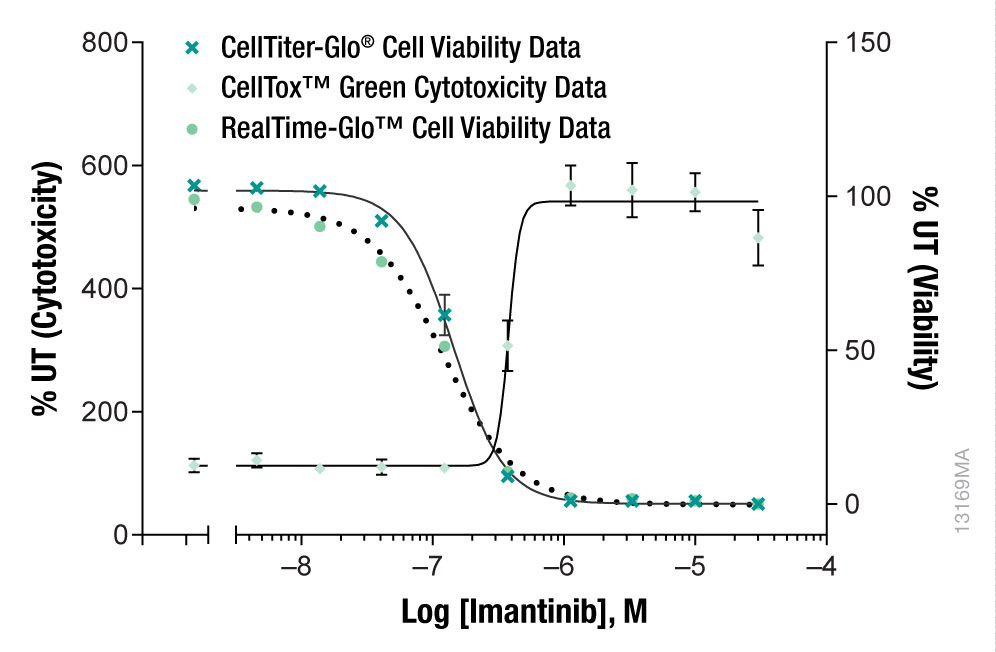
K562 (leukemic) cells were treated with Imantinib (a kinase inhibitor). The cell response was evaluated over the course of 48 hours using the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay multiplexed with the RealTime-Glo™ MT Cell Viability Assay. RealTime-Glo determines (in real time) the number of viable cells in culture by measuring the reducing potential of cells and thus metabolism (MT). At the 72-hour time point CellTiter-Glo® Cell Viability Assay Reagent was added to determine the number of viable cells by quantifying ATP.
 Interpret The Data
Interpret The DataBased on the data shown with leukemic cells, as well as the data from hepatocytes (normal cells), what can be determined about the effect of this compound on different cell types?
(Select more than one answer)
Imantinib is cytotoxic to all cellsImantinib is cytotoxic to leukemic cells
Imantinib affects viability in all cells
Imantinib is effective at killing cancer cells, but not normal cells
Check Your Answer
 Drew Explains The Answer
Drew Explains The AnswerEvaluating On-Target Potency of Imantinib
