Comparing Manual and Automated Genomic DNA Purification Methods for Genotyping Arrays
Trista Schagat, Doug Wieczorek, Christine Helt, Don Smith, Doug White and Eric Vincent
Promega Corporation
Publication Date: January 2013
Abstract
Introduction
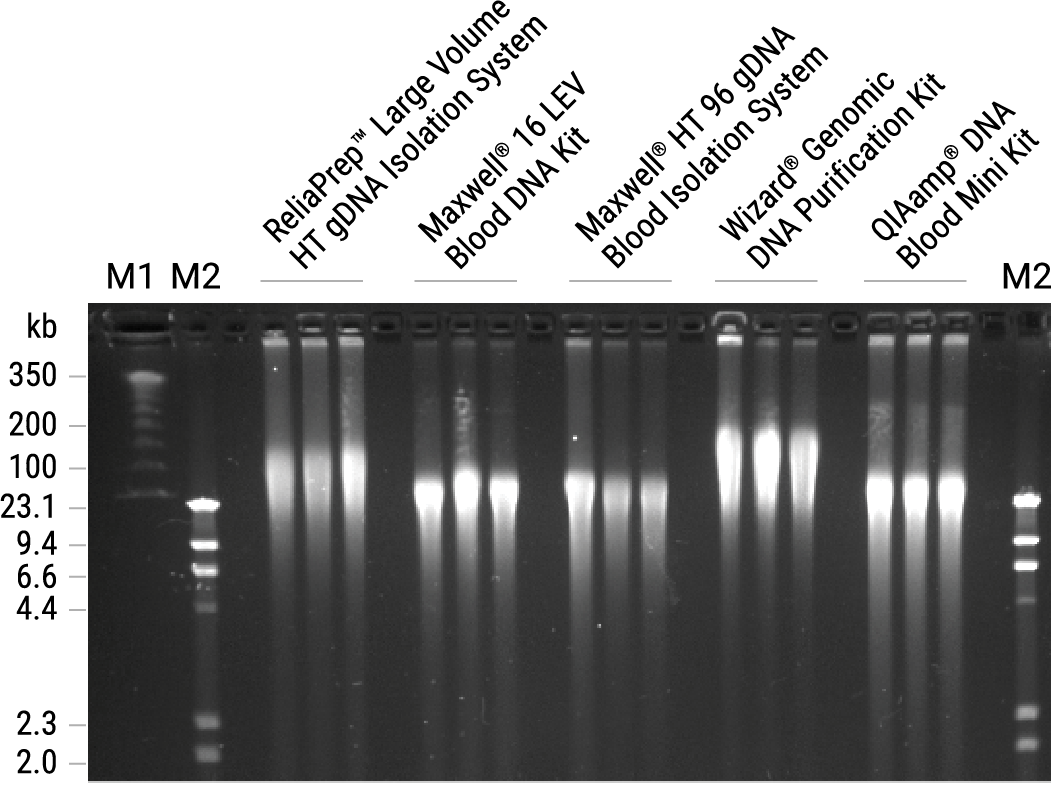
Figure 1. CHEF gel electrophoresis analysis of gDNA isolated from blood. Genomic DNA (0.5µg) was isolated from blood samples in triplicate using each system and analyzed on a 1% agarose gel using the CHEF Mapper® (BioRad). Genomic DNA was stained with ethidium bromide and compared to two molecular weight ladders: M1, ProMega-Markers® Lambda Ladders (Cat.# G3011) and M2, Lambda DNA/HindIII Markers (Cat.# G1711).
Here we compare the new Promega cellulose-based gDNA purification systems to traditional silica and precipitation-based chemistries by isolating gDNA from human blood or buccal swabs for microarray analysis. DNA purity and concentration were evaluated by absorbance spectroscopy. Samples that met the minimum concentration requirements were submitted to the Genomics Core Facility at the Medical College of Wisconsin for analysis using the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0. All samples generated results that exceeded the existing quality control standards for the core facility.
Genomic DNA Purification Systems
Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System
The Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System uses a novel cellulose-based purification method to isolate gDNA from up to 200µl of whole blood (2) . The binding matrix and chemistry allow samples to be processed in a microcentrifuge without using ethanol or isopropanol in any of the purification solutions. Genomic DNA is recovered in as little as 30µl of nuclease-free water.
Maxwell® 16 LEV Blood DNA and Buccal Swab LEV DNA Purification Kits
The Maxwell® 16 LEV Blood DNA and Maxwell® 16 Buccal Swab LEV DNA Purification Kits are used with the Maxwell® 16 Instrument to provide an easy method for efficient, automated purification using the MagnaCel™ cellulose magnetic resin (3,4). The Maxwell® 16 Instrument is supplied with preprogrammed purification procedures and is designed for use with the predispensed reagent cartridges for maximum simplicity and convenience. After an initial proteinase K treatment, the instrument can process up to 16 samples in approximately 45 minutes. The purified DNA can be used directly in a variety of downstream applications including qPCR and HLA testing. The system is recommended for up to 400µl of blood or 1–2 buccal swabs. Genomic DNA can be eluted in volumes as small as 50µl.
QIAamp® DNA Blood Mini Kit
QIAamp® DNA Blood Mini Kit (Qiagen) provides silica-membrane-based DNA purification. Mini kits are designed for processing up to 200μl of human whole blood, and DNA is eluted in a final volume of 50–200µl.
Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit
The Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a simple, solution-based method for isolating DNA from white blood cells, tissue culture cells, animal tissue, plant tissue, yeast or Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. DNA purified with this system is suitable for many applications, including amplification, digestion with restriction endonucleases and membrane hybridizations. This protocol uses alcohol precipitation of the gDNA for recovery and can be scaled up from a starting volume of 50µl of sample.
ReliaPrep™ Large Volume HT gDNA Isolation System
The ReliaPrep™ Large Volume HT gDNA Isolation System isolates gDNA from blood samples ranging from 3–10ml in a scalable format. The MagnaCel™ cellulose chemistry eliminates tedious centrifugation steps as well as the use of hazardous chemicals, which are inherent in precipitation-based chemistries. The system has been automated on the Tecan Freedom EVO® liquid-handling workstation, allowing walkaway purification of gDNA from 32 or 64 samples of 3–10ml of whole blood in 4.5 or 6 hours, respectively, regardless of sample storage or shipping conditions (5,6). For low-throughput isolation of gDNA from less than 32 samples at one time, the ReliaPrep™ LV 32 HSM Instrument can be used in a manual mode, where the user performs the pipetting functions.
Methods
Blood samples were collected in standard EDTA-containing Vacutainer® tubes. Buccal samples were collected on Puritan cotton-tipped swabs. Miniprep purifications were pooled from 3 independent donors. Large-volume purifications were from the same donor using 3 different volumes (3, 6 and 10ml). Samples were processed following the manufacturers’ directions (summarized in Table 1). The Qiagen purification system required the addition of ethanol to its wash buffer. In addition, both the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit and the ReliaPrep™ Large Volume HT gDNA Isolation System also required user-supplied alcohols, while the Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation and Maxwell 16® Systems required no additional materials to be supplied by the user. The ReliaPrep™ Large Volume HT gDNA Isolation System was used in manual mode.
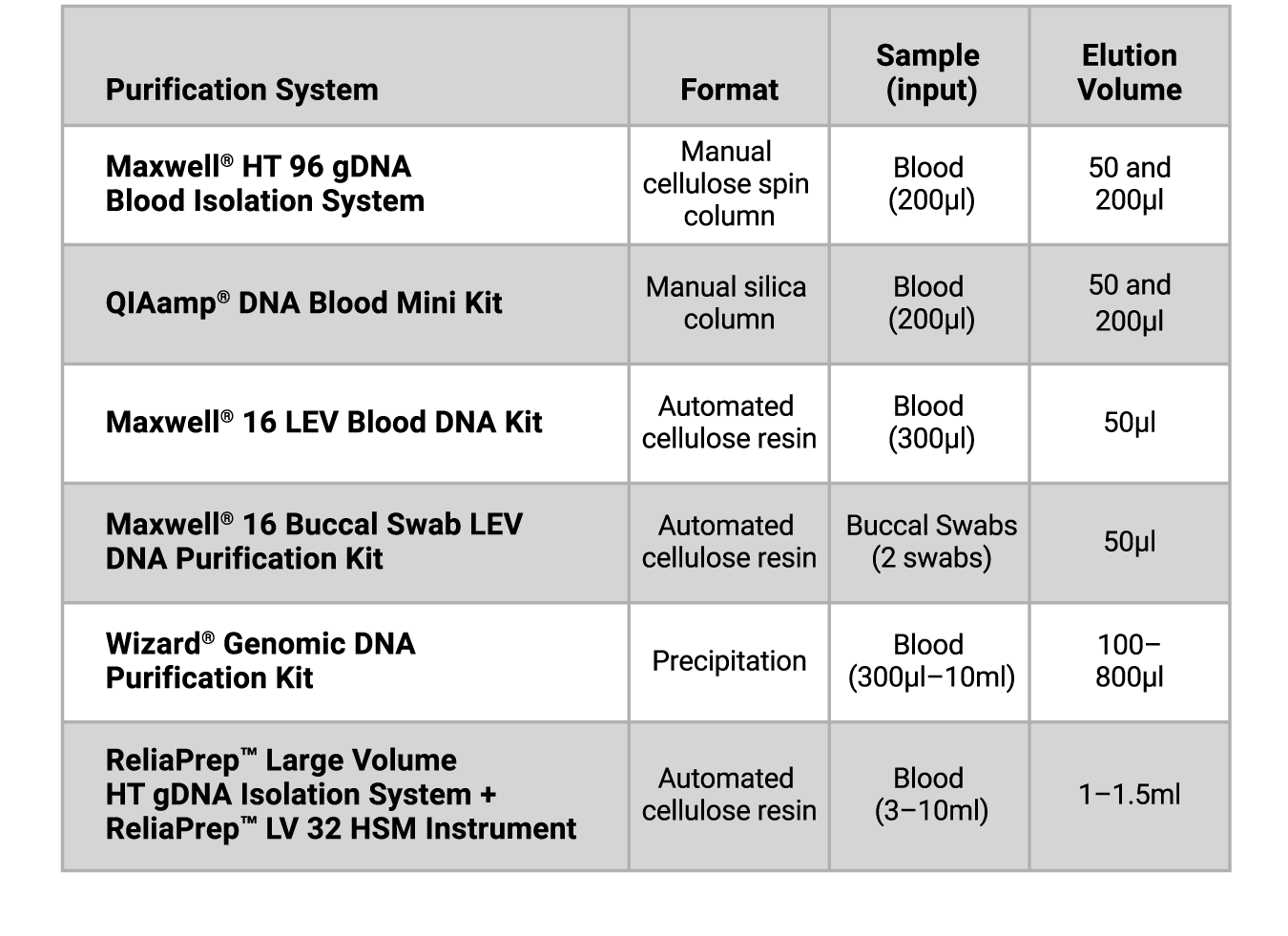
Table 1. Blood and Buccal Swab DNA Purification Kits Tested.
DNA was eluted in Nuclease-Free Water or TE, according to the manufacturers’ recommendations. Manual spin column preps used 50 and 200µl elution volumes. Elution volumes for scalable kits were adjusted based on the input volume as follows: Wizard® Genomic, 100µl elution for 300µl inputs, 250µl for 3ml, 600µl for 6ml and 800µl for 10ml; ReliaPrep™ Large Volume HT, 1ml elution for 3 and 6ml input and 1.5ml for 10ml. Genomic DNA yield and purity were determined by UV absorbance spectroscopy using a NanoDrop® 1000. Genomic DNA from blood samples was analyzed further for integrity by clamped homogenous electric fields (CHEF) gel electrophoresis (Figure 1). All samples that met the minimum required concentration (50ng/µl) were analyzed using Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 following standard protocols. Briefly, DNA was digested with NspI or StyI, adapter-ligated, amplified, fragmented and end-labeled using the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Nsp/Sty Assay Kit 6.0 and hybridized to the Genome‐Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 following standard protocols (7). Data were analyzed and genotype data quality assessed using Genotyping Console™ and Birdseed Software (Affymetrix).
Results
All miniprep systems isolated gDNA at the concentration needed for Affymetrix array analysis (≥50ng/µl; Figure 2, Panel A), although ReliaPrep™ Blood and QIAamp® DNA Blood Systems both required elution at the low end of the recommended range (50µl and 200µl, respectively; elution data not shown). Genomic DNA yields from the buccal swab samples were highly variable, but all three samples extracted with Maxwell® 16 System had a concentration greater than that required for array analysis (>50ng/µl). The large-volume isolations using 3–10ml of blood also all exceeded the minimum gDNA concentration needed (Figure 2, Panel B).
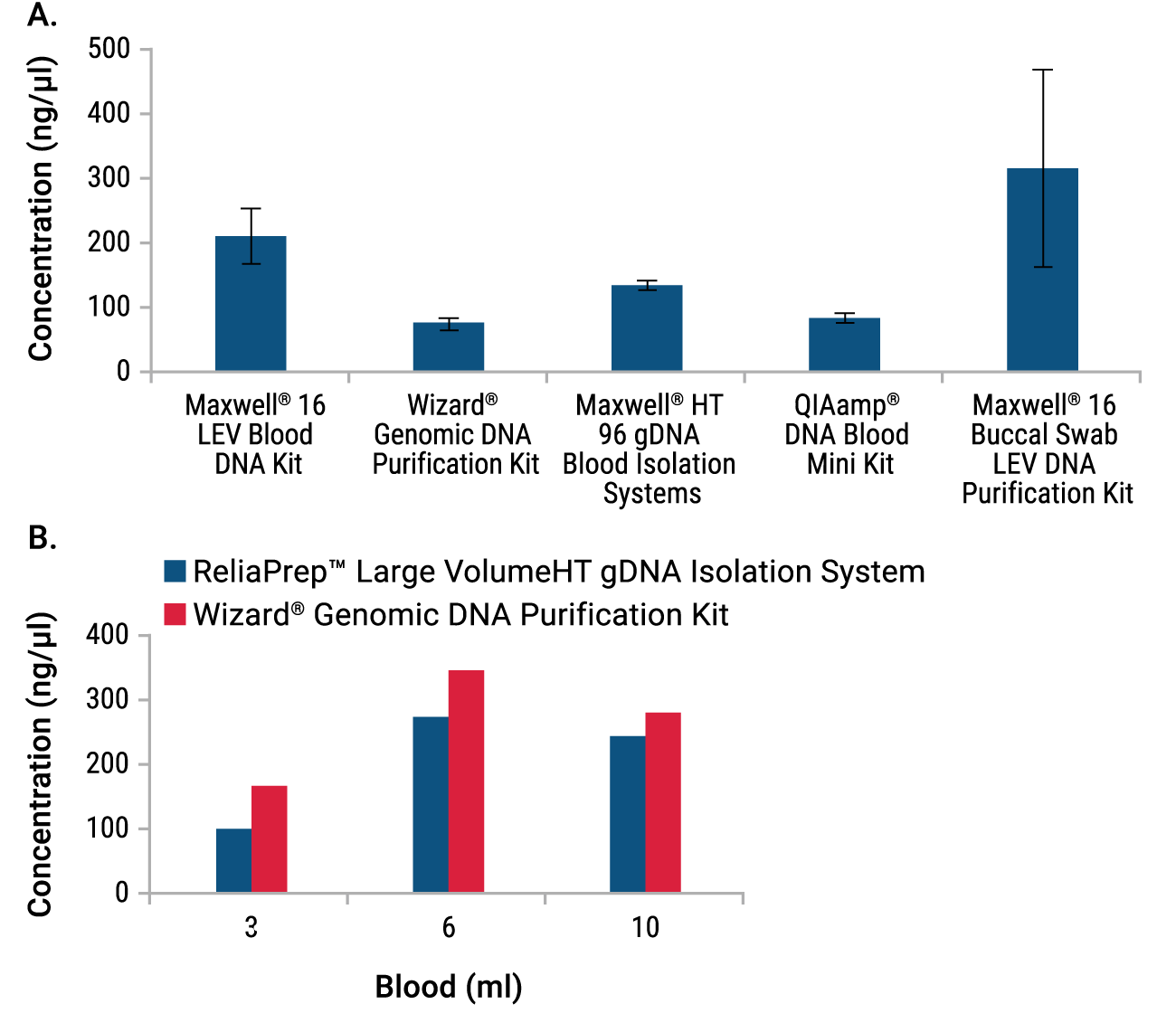
Figure 2. Concentration of gDNA Isolated from blood or buccal swabs in miniprep or large-volume format. Data from miniprep purifications (Panel A) are the average of triplicate purifications ± standard deviation. Large-volume purification data (Panel B) are single representative purifications. The gDNA concentration for each sample was evaluated by UV absorbance.
The purity of the isolated gDNA was assessed by absorbance ratios. Typically pure gDNA is defined by A260/A280 ratios of 1.8–2.2 and A260/A230 ratios of greater than 1.7. All the gDNA samples fell within the acceptable A260/A280 range; however, several samples exhibited A260/A230 readings outside of the desired range (Figure 3). All three of the Qiagen samples had A260/A230 ratios below 1.6 (data not shown). One Maxwell® 16 LEV Buccal Swab DNA Purification Kit sample also had a low reading. All of the large volume samples had absorbance ratios within the desired range. Despite the marginal purity of some of the samples, they all were submitted for analysis.
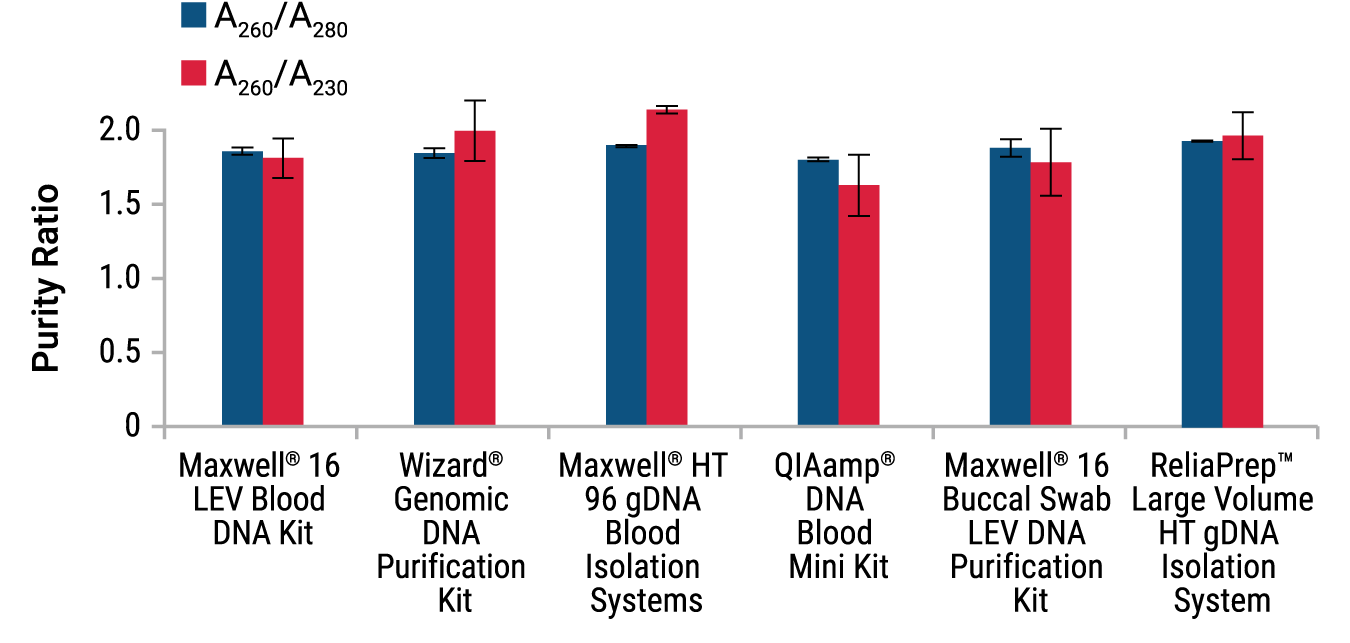
Figure 3. Purity ratios of all DNA types isolated for Affymetrix Array analysis. UV absorbance measurements at 260, 280 and 230nm were measured for all samples and average ratios ± standard deviations graphed. The Wizard® Genomic DNA and ReliaPrep™ Large Volume HT gDNA were averaged for all input volumes tested.
Samples were analyzed using the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 (7). DNA fragmentation prior to labeling and array hybridization is a critical step to obtain quality results (7). Agarose gel analysis of DNA fragmentation indicated all DNA was of the desired molecular weight (<180bp, Figure 4). All samples gave >95% QC call rate with most being approximately 97–98% (Table 3). Using the Birdseed v2 software, a Quality Control (QC) call rate can be determined. This indicates the percentage control SNPs successfully called in NspI fragments only, StyI fragments only and combined Nsp I and Sty I fragments. Data sets <90% are considered potentially problematic. All samples gave >95% Quality Control (QC) call rate with most being 97–98% (Table 2).
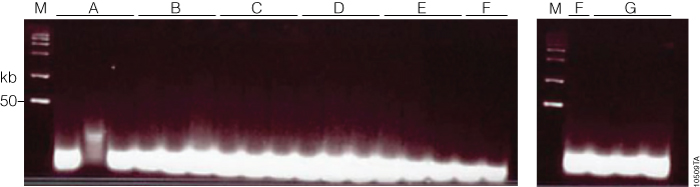
Figure 4. Fragmentation QC gel. After restriction digest, adaptor ligation, amplification and clean-up, samples were fragmented prior to labeling and hybridization as part of the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 Array protocol. To confirm that the fragmentation was uniform and that the resulting fragments were <180bp, each sample was run on a 4% TBE gel. All samples were below the lowest band of the ladder (50bp). Lane A, Maxwell® 16 Buccal Swab LEV DNA Purification Kit; lane B, Maxwell® 16 LEV Blood DNA; lane C, Qiagen QIAamp® Blood Mini Kit; lane D, Maxwell® HT 96 gDNA Blood Isolation System; lane E, Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit (200µl blood); lane F, ReliaPrep™ Large Volume HT gDNA Isolation System (3, 6, 10ml blood); lane G, Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit (3, 6, 10ml blood). Buccal sample #2 (lane A) was lost during preparation, and the sample was repeated and performed equivalent to the other samples.
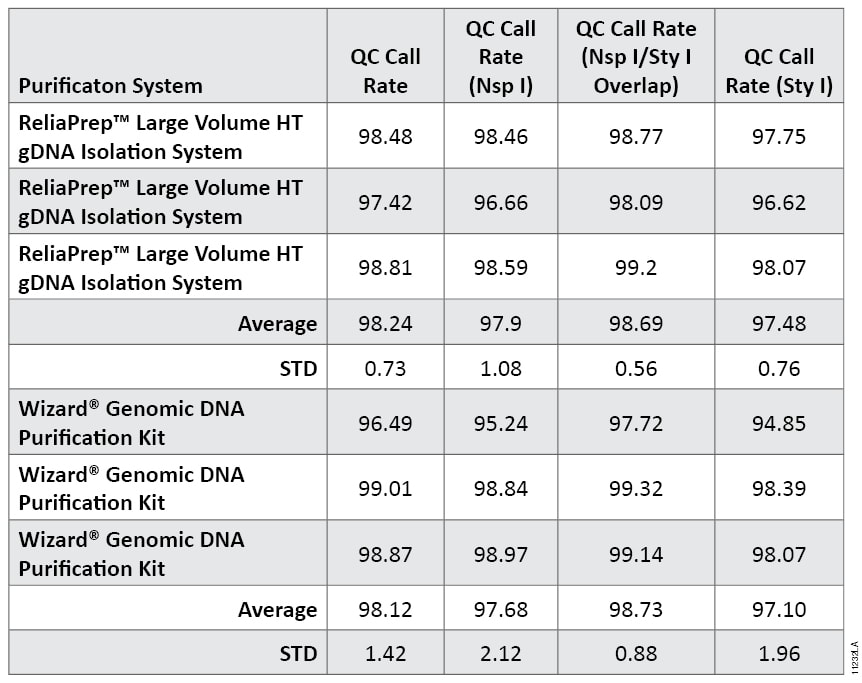
Table 2. Quality Control (QC) Call Rates for DNA Samples Processed by Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0. The percentage control SNPs successfully called in Nsp I fragments only, Sty I fragments only and combined Nsp I and Sty I fragments are shown. Data are the average and standard deviation of triplicate samples processed for each purification kit. Percent success of Nsp- and/or Sty-digested control DNAs are indicated as QC call rates.
Summary
of genomic DNA from blood and buccal swabs worked as well as, or better than, traditional precipitation-based or silica-based purification methods.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Ulrich Broeckel and lab at the Human and Molecular Genetics Center, Medical College of Wisconsin, for the processing and analysis of the Affymetrix microarrays.
All of the gDNA systems we tested yielded DNA of sufficient concentration and purity for analysis, and met the core facility standards for array processing, and were compatible with array analyses using the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0. The Promega cellulose-based miniprep and large-volume purification systems for manual and automated purification
References
- McCaroll, S.A. et al. (2008) Integrated detection and population-genetic analysis of SNPs and copy number variation Nat. Gen. 40, 1166–74.
- Smith, D. et al. (2011) ReliaPrep Blood gDNA Miniprep System a Novel Column Based Purification of gDNA from Whole Blood. Promega Corporation Website accessed November 14, 2012.
- Mandrekar, P.V. et al. (2010) High-Concentration (>100ng/µl) Genomic DNA From Whole Blood Using the Maxwell® 16 Low Elution Volume Instrument. Promega Corporation Website Accessed June 7, 2012.
- Gorshe, R. et al. (2010) Automated DNA Purification from Buccal Swabs for qPCR and HLA Typing assays using the Maxwell® 16 LEV Blood Kit. [Scientific Poster] Promega Website Accessed June 7, 2012.
- (2011) Tecan Promega ReliaPrep 32 Extraction Tecan Website (registration required) Accessed June 7, 2012.
- (2011) Tecan Promega ReliaPrep Extraction Extraction, Quantitation and Normalisation Workstation Tecan Website (registration required) Accessed June 7, 2012.
- (2012) Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Nsp/Sty 6.0 User Guide Affymetrix website Accessed June 8, 2012.