Improved Protein Digestion with the Sequencing Grade Endoproteinases Chymotrypsin and Lys-C
Dan Simpson, Sergei Saveliev, Becky Godat and Ashley Goodman
Promega Corporation
Abstract
Protein digestion by trypsin is an integral part of protein sequencing and identification by mass spectrometry. However, trypsin can cleave protein into peptides that are too large or too small to provide good sequence information. As well, the proximity of post-translational modifications to proteolytic sites can interfere with protease efficiency. It is becoming common practice to use alternative proteases to extend proteomic coverage for bottom-up protein identification. This article describes the use of two alternative proteases for mass spectrometric analysis.
Introduction
Mass spectrometry has become a routine method for the identification and characterization of proteins present over a wide range of concentrations in complex biological matrices. In most cases identification is done by a bottom-up approach where the protein is first digested into peptides using a protease, then measured by mass spectrometry (MS) and matched to known peptide sequences through algorithm-based search. Since searching constrains protein sequences to peptides that match predicted protease specificity, it is critical for identification that the protease be highly precise to produce a data set synchronized with the search parameters. This requirement for high specificity necessitates the use of highly purified proteases.
In most cases the protease used is trypsin. Trypsin cleaves at the C-terminus of lysine and arginine with both high efficiency and specificity (1). Trypsin is also preferable to other proteases because it produces peptides of practical length and favorable charge, well suited for tandem MS sequencing by collision-induced dissociation (CID).
However, the use of trypsin or any other single protease does not provide complete proteomic coverage, and there are many examples where trypsin cleavage can result in peptides that are too small (<6 amino acids) or too large to provide substantive sequence information . Additionally, the proximity of proteolytic sites to post-translational modifications (PTM) can alter protease efficiency at these sites, potentially hindering detection of the PTM (2–3). For these and other reasons, it is a common practice to use alternate proteases to extend proteomic coverage for bottom-up protein identification and for mapping of post-translational modification (3–4).
Two alternatives to trypsin that have seen substantial use in protein identification and characterization are endoproteinase Lys-C and chymotrypsin.
Two Trypsin Alternatives
Two alternatives to trypsin that have seen substantial use in protein identification and characterization are endoproteinase Lys-C and chymotrypsin. Chymotrypsin is orthogonal to trypsin in specificity, cleaving most frequently on the carboxyl side of hydrophobic aromatic amino acids phenylalanine (F), tryptophan (W) and tyrosine (Y) and at a lower rate the carboxyl side of leucine (L) (5). In contrast, endoproteinase Lys-C cleaves at the carboxyl side of lysine only.
In this article, we introduce sequencing grade versions of endoproteinase Lys-C and chymotrypsin, for use in mass spectrometry-based identification and characterization of proteins, and demonstrate their use with in-solution and in-gel applications.
Sequencing-Grade Chymotrypsin
Sequencing-Grade Chymotrypsin (Cat.# V1061) is a serine endopeptidase isolated and purified from bovine pancreas. It cleaves at the carboxyl terminus of phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan and leucine (5). To demonstrate the use of chymotrypsin for extending protein coverage, we denatured and digested the Universal Proteomics Standard Set 48 protein mixture (UPS1; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) with Trypsin Gold (Cat.# V5280) and chymotrypsin under identical denaturing conditions and compared sequence coverage at the protein level for these two digests. Figure 1 shows the percentage of protein coverage observed for the top 12 proteins identified with trypsin (in blue). For most proteins in this mixture, trypsin gave the highest level of coverage under the reaction conditions defined in this experiment.
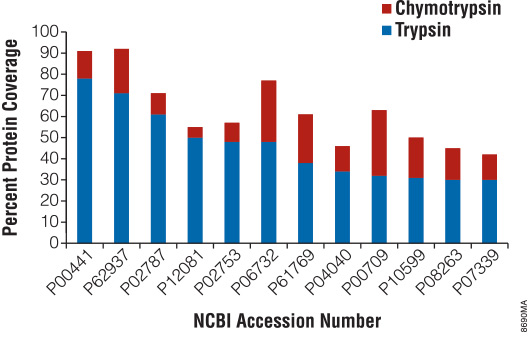
However, digestion with chymotrypsin provided additional coverage for all of the top 20 proteins identified. In all cases, some part of the coverage observed with chymotrypsin was unique and extended the number of amino acids detected for both enzymes on average by approximately 40% (Figure 1). The largest increase observed (catalase, P00709 in Figure 1) was greater than 90%.
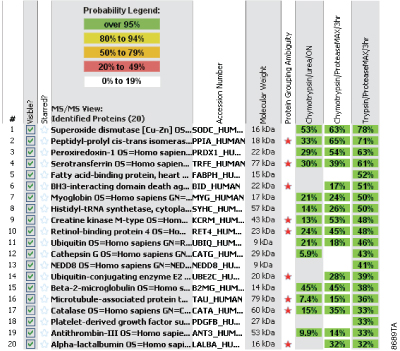
Efficient protein digestion normally requires denaturation of the protein(s) to be digested and compatibility of the protease with the denaturing environment used for digestion. Mass spectrometry compatible labile surfactants such as the recently introduced ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant (Cat.# V2071) are an effective option for denaturation of proteins in solution. To confirm that Chymotrypsin is compatible with ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant and demonstrates enhanced protein digestion we also used the UPS1 standard mixture. We compared sequence coverage obtained using ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant in a digestion reaction to that obtained using 8M urea. Figure 2 demonstrates that ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant as an in-solution denaturant does not inhibit Chymotrypsin and in fact gives improved protein coverage compared to 8M urea for this standard protein mixture under the defined reaction conditions. With just two exceptions the coverage observed for ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant was significantly greater than that observed with urea.
Endoproteinase Lys-C
Sequencing-Grade Endoproteinase Lys-C is a highly purified serine protease derived from Lysobacter enzymogenes, that cleaves specifically at the carboxyl terminus of Lysine. To demonstrate the use of Lys-C for improved protein analysis, we first confirmed its high cleavage specificity by over-digesting the 2.8kDa peptide Melittin (GIGAVLKVLTTGLPALISWIKRKRQQ) at a 1:10 Lys-C to substrate ratio (wt/wt). Lys-C digestion of melittin gave rise to four peptides, two (RK and RQQ) that were unretained on the C-18 reverse-phase LC column and two peptides that were retained as observed in Figure 3.

Comparisons of the digest at 1 hour and at 18 hours demonstrate that the initial peptide products (at 16 and 24 minutes) remain intact (more than 95%) and are not subject to any further digestion by the high concentration of endoproteinase Lys-C present in the reaction over the 18-hour incubation.
Use of endoproteinase Lys-C for improved protein analysis was demonstrated with a mouse protein digested in-gel. Protein extract from mouse heart tissue was resolved with SDS-PAGE, and a protein band with an apparent electrophoretic mobility of 48–50 kDa was excised from the gel. The protein was digested in-gel with trypsin or endoproteinase Lys-C. The digests were analyzed with MALDI-TOF/TOF as described in the legend for Figure 4. To improve recovery of peptides from gel, we digested the protein in the presence of ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant. The protein was identified as ubiquinol cytochrome c reductase.

The data showed that use of Lys-C as alternative complementary protease increased protein coverage. Indeed, combination of trypsin and Lys-C increased the reductase coverage 1.3-fold as compared to the coverage obtained with trypsin alone (Figure 4). A significant share of the increase came from Lys-C peptides that represented extended versions of peptides identified in the tryptic digest (see Lys-C peptides 43–66, 163–183 and 232–250). Lys-C skipped arginine residues and cleaved at downstream lysine residues, effectively increasing peptide length up to twofold.
Summary
In general, our data show that Endoproteinases Chymotrypsin and Lys-C are a valuable addition to trypsin for the purpose of improved protein analysis by mass spectrometry. Promega Sequencing-Grade Endoproteinases Chymotrypsin and Lys-C demonstrate a high specificity required for proteases used in mass spectrometry protein sample preparation.
References
- Olsen, J.V., Ong, S. and Mann, M. (2004) Trypsin cleaves exclusively C-terminal to arginine and lysine residues. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 3, 608–14.
- Winter, D. et al. (2009) Protein phosphorylation influences proteolytic cleavage and kinase substrate properties exemplified by analysis of in vitro phosphorylated Plasmodium faciparum glideosome-associated protein 45 by nano-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 393, 41–7.
- Garcia, B.A. et al. (2004) Characterization of phosphorylation sites on histone H1 isoforms by tandem mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 3, 1219–27.
- Mohammed, S. et al. (2008) Multiplexed proteomics mapping of yeast RNA polymerase II and III allow near-complete sequence coverage and reveals several novel phosphorylation sites. Anal. Chem. 80, 3584–92.
- Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (2010) Peptide Cutter ExPASy Proteomics Server Website.
Mass Spectrometry Tools
Related Resources
Protein Purification and Analysis Guide
This guide is a comprehensive primer for protein purification and analysis methods with detailed protocols and references.
What's New in Bottom-Up Proteomics?
This article contains several references that provide insight into new discoveries and researchers' recommendations for extraction and digestion.